Cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage: how automation and calculations work for you
Cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage is a strategy that allows traders to earn regardless of market direction. In this article, we explain how pair trading works, what correlation, beta coefficient, cross rate, and Z-score are, and also provide a practical example using Resonance platform tools. You will learn how complex calculations help traders make more accurate decisions.
Table of content
- 01Introduction
- 02How statistical arbitrage trading works in the crypto market
- 03Choosing pairs of assets for cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage
- 04Searching for price discrepancies
- 05Using analytical tools in pair trading
- 06Advantages of cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage
- 07Risks and limitations
- 08Conclusion
Introduction
Traders are constantly looking for strategies that allow them to reduce risks and earn steadily even in the highly volatile crypto market. One of these techniques is considered cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage. In essence, it is pair trading, where the trader works not with a trend, but with mathematics and historical data.
The essence of pair trading: two assets are selected that historically move synchronously. When coin prices temporarily diverge, opposite positions are opened. When prices return to the average value, the trader fixes a profit.
This strategy has gained popularity because it is relatively neutral to market direction: you can profit both on growth and on decline.
How statistical arbitrage trading works in the crypto market
Statistical arbitrage trading is a strategy built on using temporary discrepancies in the prices of two assets that have historically moved synchronously and have a high correlation.
Correlation shows how synchronously two cryptocurrencies move. The value is measured from –1 to +1:
- +1 means complete coincidence of movements
- 0 — no connection
- –1 — assets move in opposite directions
For cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage, a high positive correlation (0.7 and above) is important.
Choosing pairs of assets for cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage
The first step is to select a suitable pair of coins. As a rule, these are coins from the same sector (for example, DeFi projects, AI sector, competing blockchains, etc.) that have a logical fundamental connection: without it, the probability of a correlation break increases sharply.
Choosing the right pairs of coins is the key to the success of the strategy. Usually, traders take assets:
- from the same sector with a similar business model
- with high liquidity
- with similar market drivers
For example, let’s take the SUI/SEI pair. These coins can be considered as a pair for cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage, since they are two coins close in fundamentals with high correlation.
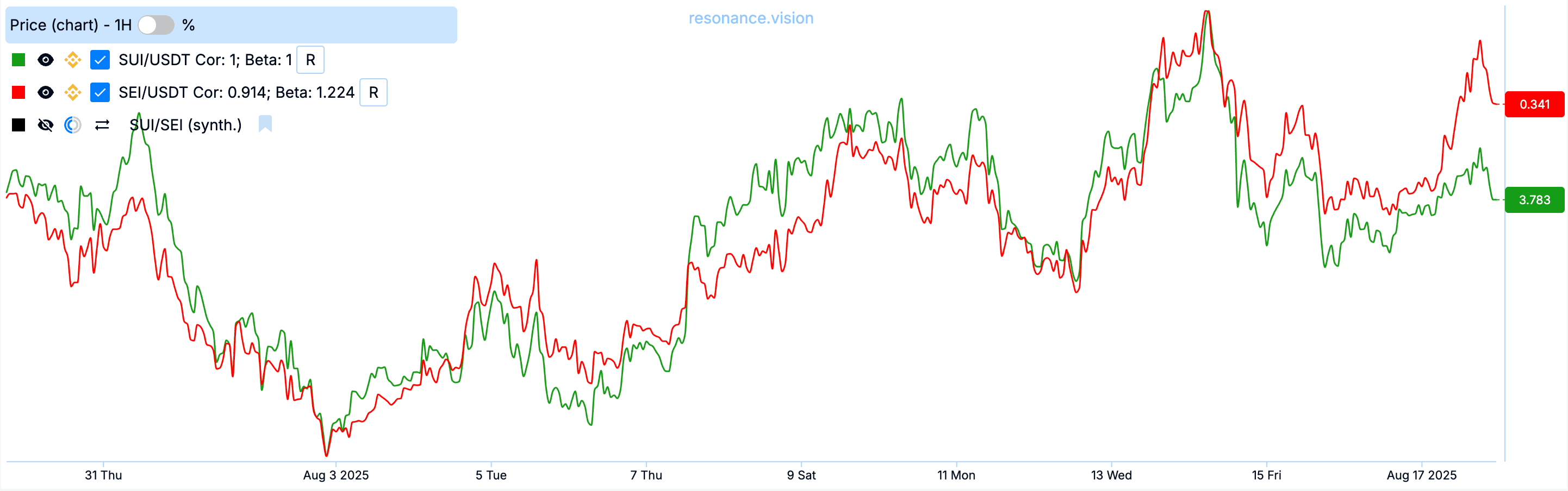
The correlation of these coins is high — 0.90, which is perfect for pair trading.
It is also important to pay attention to how volatile the selected coins in the pair are relative to each other. For this, the beta coefficient is calculated.
Beta coefficient shows the ratio of volatility between assets. Simply put: how much one asset changes relative to another.
- If β = 1 → both assets have approximately the same volatility
- If β > 1 → the asset is more volatile than the base
- If β < 1 → the asset has lower volatility than the base
In pair trading, it is important that β is approximately the same for both coins you take into a pair. Then risks are more predictable, and discrepancies in the cross rate can be assessed more objectively.

Searching for price discrepancies
After choosing a pair, the trader monitors the dynamics of price divergence between assets. For this, a synthetic chart of the price ratio of two coins — the cross rate — is used.
In pair trading, the cross rate means a chart of the price ratio of two assets. It allows you to clearly see how far the coins have diverged in price and when there is a chance to return to the mean.
If the cross rate deviates too much, a trading opportunity arises: a long position is opened on the undervalued asset and a short on the overvalued one. As soon as prices return to the statistical average, positions are closed with a profit.
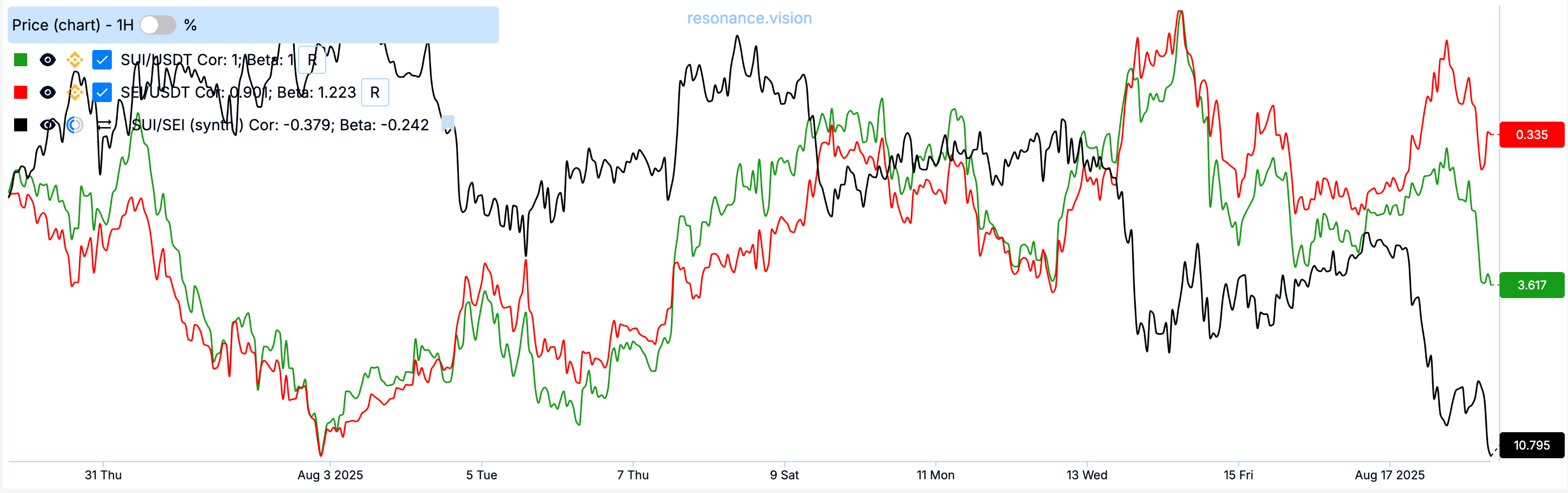
A simple comparison of prices does not give an objective picture: one asset may be more volatile, another less. Therefore, to understand how strongly the asset prices in a pair have diverged, we need an indicator that shows the anomaly of this deviation relative to history. For this, the Z-score is used.
Z-score is an indicator that reflects the degree of deviation of the current price (in this case, the cross rate) from the historical average in units of standard deviation.
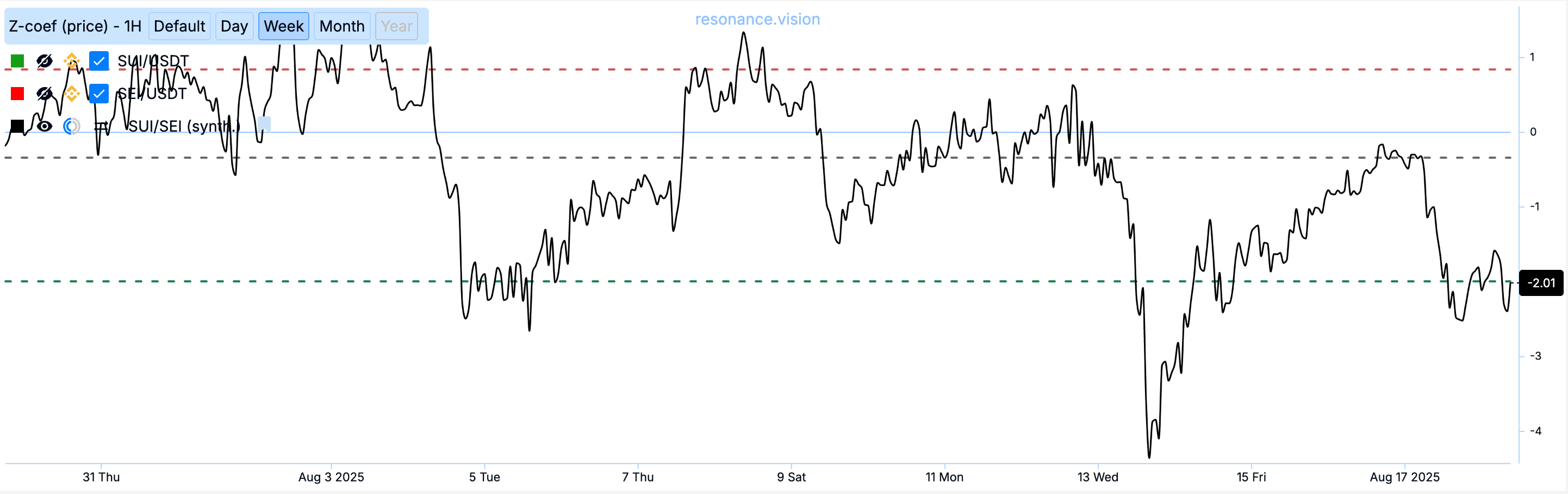
- If Z-score is close to zero — there is no discrepancy between prices
- If Z-score > +2 or < –2 — the deviation is considered anomalous, and the probability of prices returning to the average increases
Let’s examine the standard deviation of our SUI/SEI pair in absolute values (here we are only looking at the average maximum deviation magnitude, without direction). We see that over the past month, the weekly standard deviation was significantly above 2 only once, generally not exceeding 2.58 standard deviations.
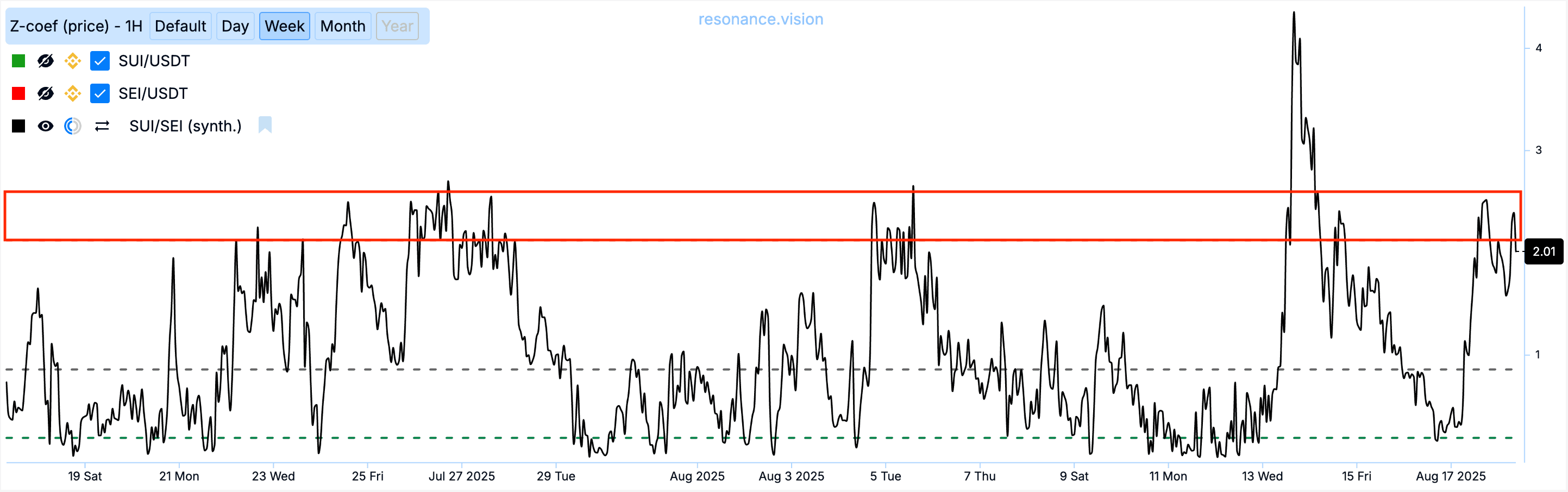
At the moment, there is an opportunity to open a trade, as the standard deviation of the cross-rate is anomalous — 2.11.
We open a long position on SUI/USDT and a short position on SEI/USDT. When the standard deviation returns to its average value of 0, we close both positions:
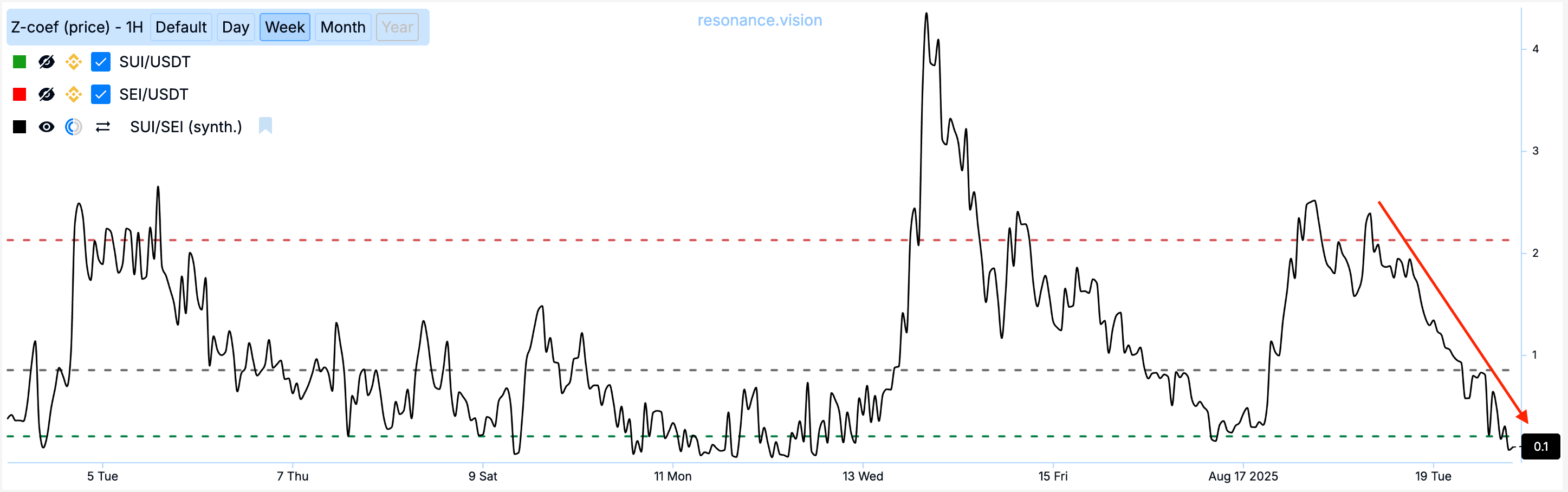
Trade result:
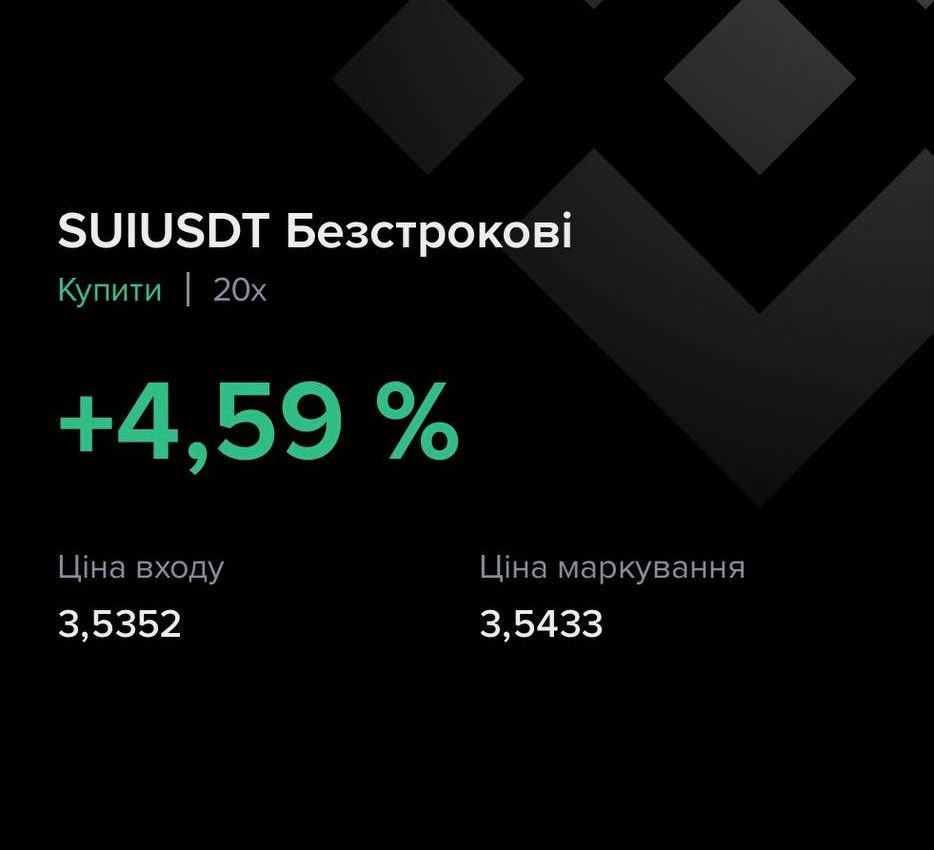
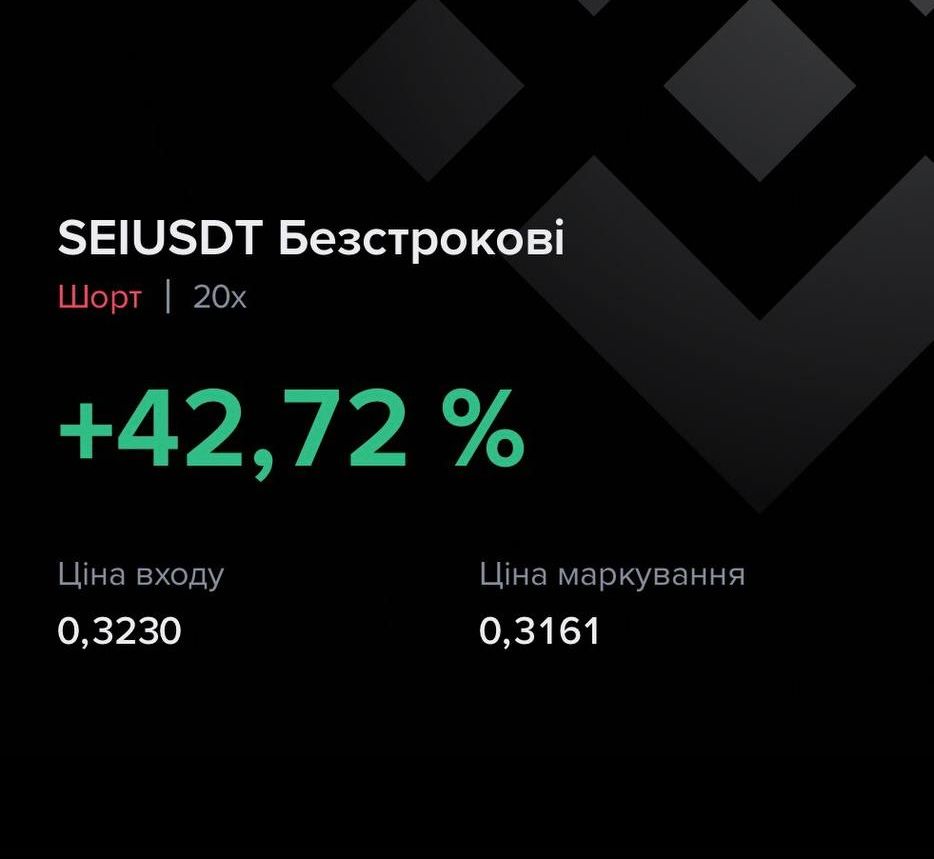
Using analytical tools in pair trading
To identify such market situations for cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage, traders use various services and analytical tools that perform complex calculations automatically and visualize them conveniently.
The MarketDelta tool on the Resonance platform:
- builds a cross rate for clear tracking of the spread dynamics between selected assets
- calculates the correlation coefficient between cryptocurrencies to see how synchronously they move and whether the pair is suitable for arbitrage
- computes the Z-score — an indicator of the anomaly of price deviations from the average, which helps determine a possible entry point into the trade
- calculates the beta coefficient — the ratio of volatility between assets
Thus, the trader does not need to manually calculate dozens of indicators — everything is performed by the platform. The task is reduced to interpreting the data and making decisions. Automatic calculations reduce the probability of error and allow you to focus on the strategy.

Advantages of cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage
- Independence from market direction. Profit can be obtained both in falling and rising markets.
- Hedging risks. Loss on one asset is compensated by profit on another.
- Flexibility in choosing pairs. Dozens of token pairs from different sectors can be used.
- Reliance on statistics, not emotions. Decisions are made based on specific numbers: correlation, standard deviation, beta coefficient.
- Applicability for different horizons. The strategy is suitable for both intraday trading and medium-term ideas.
Risks and limitations
- Break of correlation. Even historically related assets can stop moving synchronously.
- Big difference in volatility. If one token reacts more strongly, positions become unbalanced.
- Errors in analysis. Past data does not guarantee future results.
- Risk management. It is necessary to clearly define conditions for closing a losing trade.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage is a strategy that relies not on emotions and news, but on mathematics and historical data. It allows you to analyze correlation, beta coefficient, and cross rates, which means making more balanced decisions.
The main advantage is that statistical arbitrage trading remains profitable regardless of market direction. Modern platforms, services, and programs such as MarketDelta from Resonance help search for effective pairs and speed up the analysis process.
This makes the techniques of cryptocurrency statistical arbitrage accessible not only to professionals but also to those who want to systematically develop in crypto trading.
Follow new insights in our telegram channel.
No need to invent complex schemes and look for the "grail". Use the Resonance platform tools.
Register via the link — get a bonus and start earning:
OKX | BingX.
Promo code TOPBLOG gives you a 10% discount on any Resonance tariff plan.

